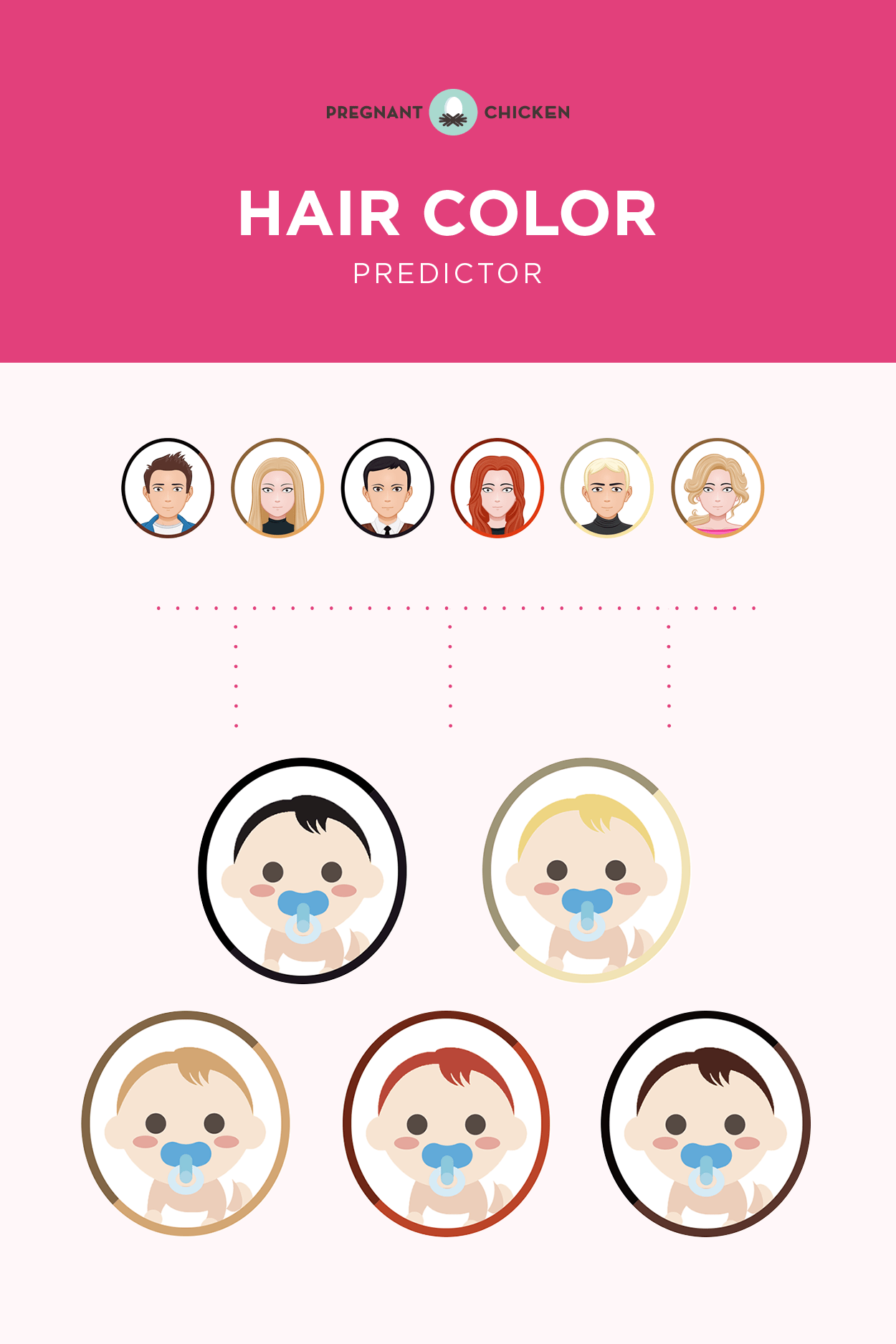
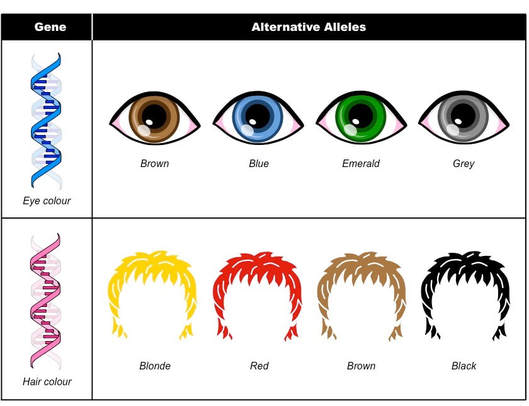
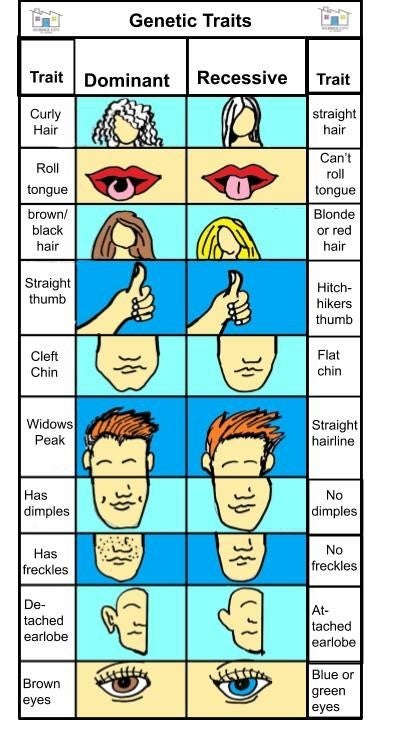
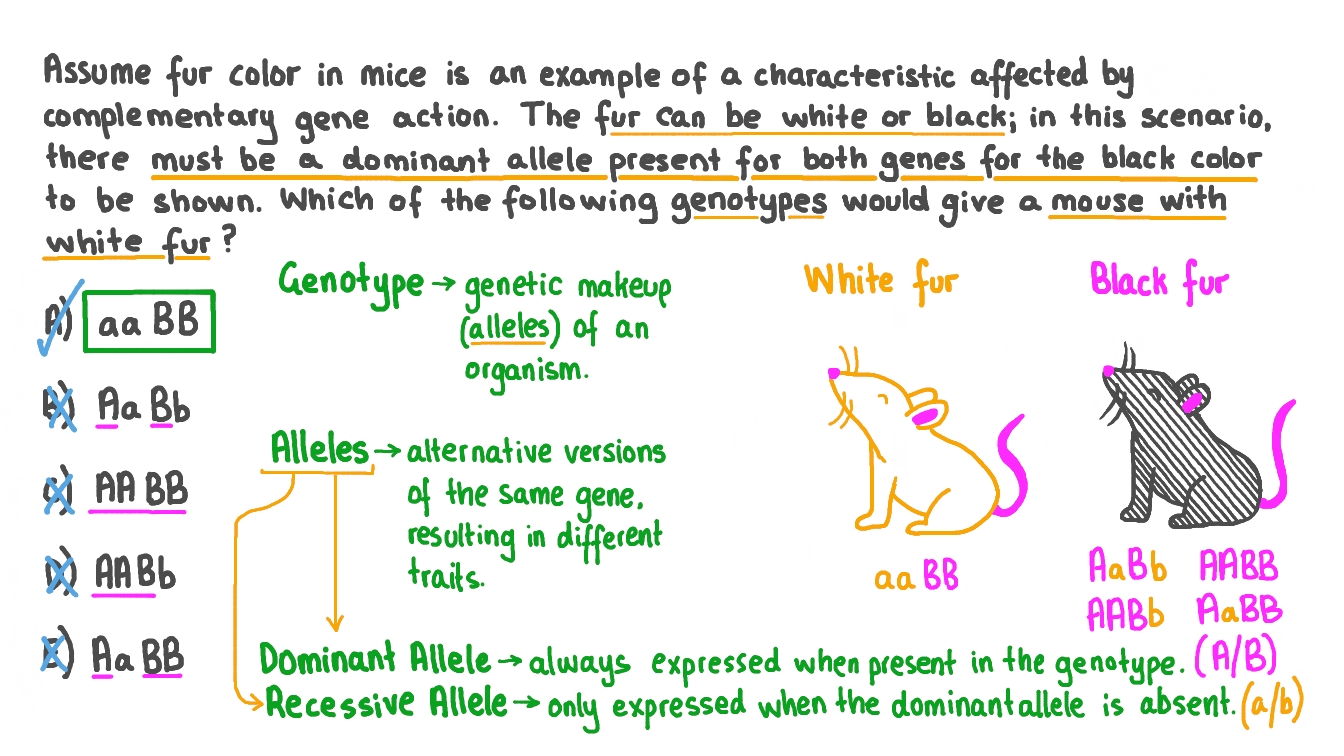
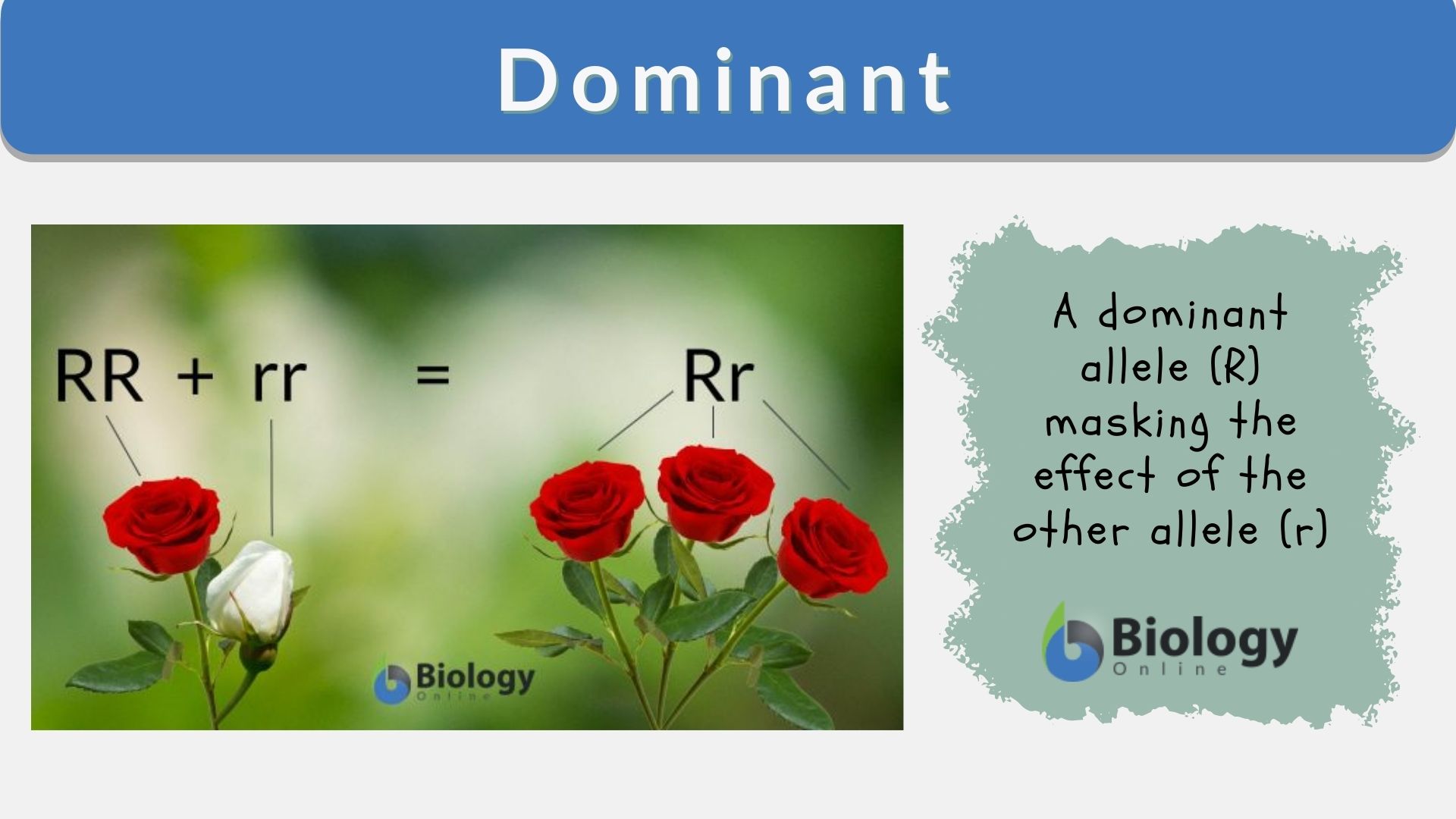
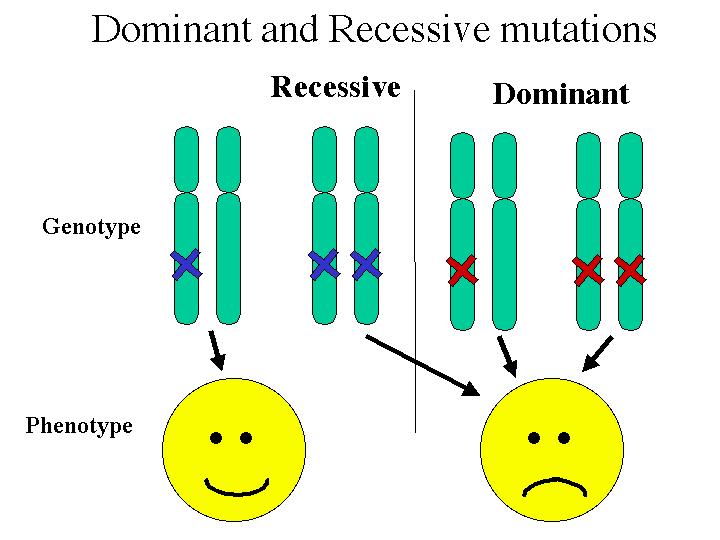
Blonde hair has long been considered a desirable and coveted trait. From Marilyn Monroe to Beyoncé, there is no denying the appeal of golden locks. But have you ever wondered what makes someone naturally blonde? The answer lies in genetics. In this article, we will explore the science behind blonde hair and the dominant genes that determine its color.Blonde Hair Genetics: Understanding the Science Behind It
Contrary to popular belief, blonde hair is not simply a result of having less melanin in one's hair. Melanin, a pigment produced by specialized cells called melanocytes, gives hair its color. Instead, the genetic basis of blonde hair lies in two key genes: MC1R and The MC1R gene is responsible for producing the protein that regulates the production of melanin. When this gene is mutated, it can lead to a reduced amount of melanin in the hair, resulting in lighter shades like blonde. On the other hand, the ASIP gene determines the distribution of melanin in the hair follicles. A variation in this gene can lead to a more dispersed distribution, resulting in a lighter overall hair color.Genetic Basis of Blonde Hair Color
Blonde hair is often associated with fair skin and light-colored eyes. This is because the same gene that determines hair color also plays a role in determining skin and eye color. The MC1R gene also regulates the production of melanin in the skin and eyes, which is why individuals with blonde hair often have lighter skin and eye colors as well. However, it is important to note that not all individuals with blonde hair have the same genetic makeup. The combination of different variations in the MC1R and Blonde Hair: The Genetics Behind the Color
Blonde hair is often referred to as a dominant trait, meaning it is more likely to be expressed in offspring. However, this is not entirely accurate. While it is true that individuals with blonde hair are more likely to have children with blonde hair, this is not solely due to genetics. Cultural and societal preferences also play a significant role in the prevalence of blonde hair. Additionally, the dominance of blonde hair can vary depending on the individual's genetic makeup. For example, a person with one copy of the MC1R gene variant may have lighter hair than someone with two copies, but this does not necessarily mean that the person with two copies will have darker hair. Other genetic and environmental factors can also influence hair color.Blonde Hair: A Dominant Trait?
The dominance of blonde hair can be attributed to the fact that the MC1R gene is a recessive gene. This means that it is masked by other genes, such as those responsible for darker hair colors. However, when both parents carry the MC1R gene variant, there is a higher chance of their offspring having blonde hair. It is also worth noting that the dominant gene for blonde hair is not universal. In some populations, variations in the MC1R gene are more common, leading to a higher prevalence of blonde hair. For example, individuals of Northern European descent are more likely to have blonde hair due to a higher frequency of MC1R gene variations.The Genetics of Blonde Hair: What Makes It Dominant?
While the MC1R gene is often associated with blonde hair, it is not the only gene that can influence hair color. Other genes, such as those involved in the production of melanin and the distribution of pigments, also play a role. This is why siblings with the same parents can have different hair colors. Furthermore, the expression of the dominant gene for blonde hair can be influenced by other factors. For example, hormonal changes during puberty can affect the production of melanin, resulting in a change in hair color. Additionally, exposure to sunlight can also cause bleaching of the hair, leading to a lighter shade.Blonde Hair Genetics: Exploring the Dominant Gene
As we have discussed, blonde hair is not entirely determined by genetics. While the MC1R gene does play a significant role in determining hair color, other factors can influence its expression. This is why blonde hair cannot be considered a purely dominant trait. In fact, the concept of dominant traits is not as straightforward as it may seem. The expression of certain genes can be influenced by a variety of factors, making it difficult to classify traits as purely dominant or recessive. Therefore, it is essential to understand that hair color, including blonde hair, is a complex combination of genes and environmental factors.Blonde Hair: Is It Really a Dominant Trait?
While the MC1R gene may not be the sole determinant of blonde hair, it is undoubtedly a crucial factor. By understanding the science behind this gene and its role in hair color, we can gain a better understanding of the genetics behind blonde hair. Furthermore, studying the genetics of hair color can also have practical applications. For example, understanding the genetics of blonde hair can help in developing more accurate hair dye products for individuals with this hair color, as well as identifying potential risks for certain genetic conditions that may be associated with blonde hair.The Science of Blonde Hair: Understanding the Dominant Gene
There are many myths and misconceptions surrounding blonde hair and its genetics. Some believe that natural blondes will eventually "outgrow" their blonde hair and that all blonde hair will eventually turn grey. However, these are simply not true. As we have discussed, the production of melanin and the distribution of pigments in the hair are complex processes that can be influenced by a variety of factors. Additionally, there is no scientific evidence to support the idea that all blonde hair will eventually turn grey. Hair color is determined by a combination of genetics, aging, and environmental factors, and each person's hair will age differently.Blonde Hair Genetics: Debunking the Myths
In conclusion, while genetics play a significant role in determining hair color, it is not the only factor at play. The MC1R and ASIP genes are responsible for regulating the production and distribution of melanin, which in turn affects hair color. However, other genes and environmental factors can also influence hair color, making it a complex and fascinating aspect of human genetics. By understanding the science behind blonde hair and its genetics, we can gain a better appreciation for this highly sought-after trait. Whether you were born with natural blonde hair or have achieved it through hair dye, there is no denying the allure of this hair color. And now, you have a deeper understanding of the genetics that make it possible.Blonde Hair: The Role of Genetics in Hair Color
Why Blonde Hair Genes are Dominant: The Science Behind Hair Color Inheritance
The Basics of Hair Color Inheritance
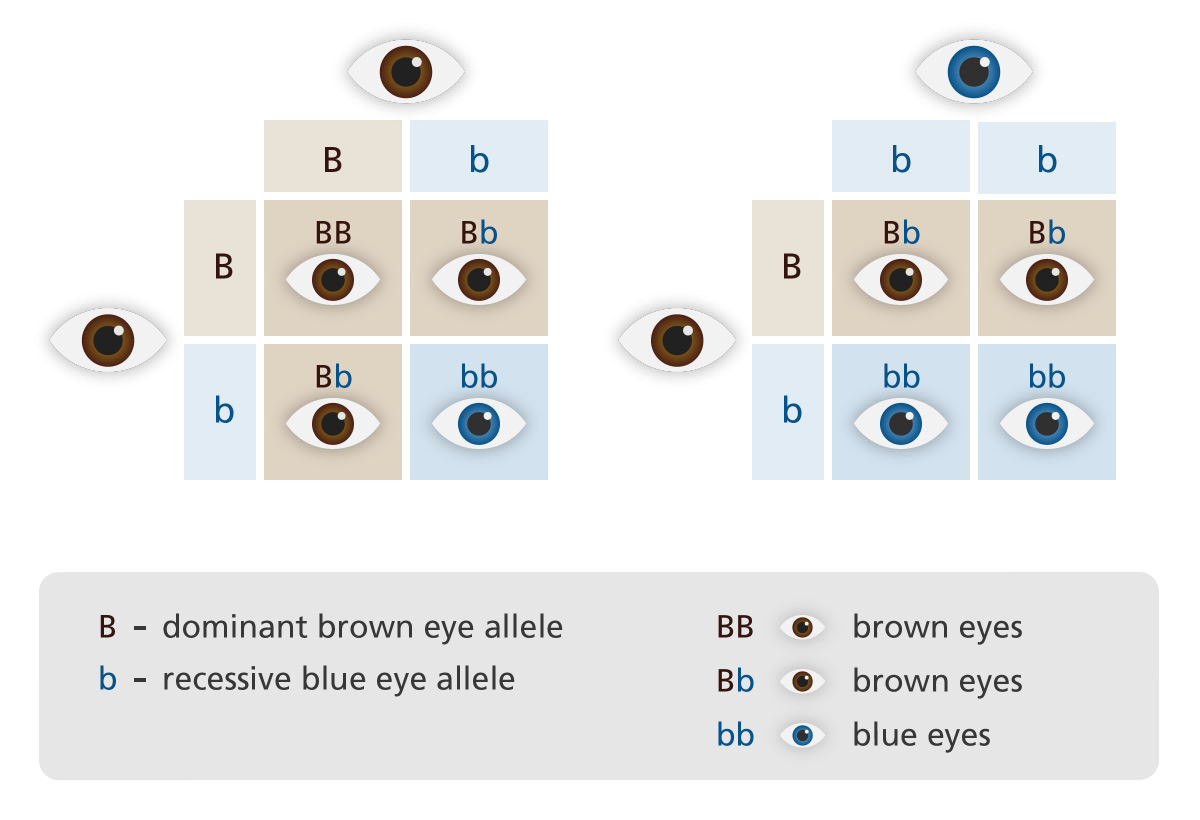 When it comes to hair color, there are a variety of genes that influence its outcome. These include the MC1R gene, which is responsible for producing the pigment melanin, and the TYRP1 gene, which plays a role in the production of eumelanin and pheomelanin. These two pigments determine the color of our hair, with eumelanin producing dark colors and pheomelanin producing red and blonde shades. However, the exact combination of these genes can vary from person to person, leading to a wide range of hair colors.
When it comes to hair color, there are a variety of genes that influence its outcome. These include the MC1R gene, which is responsible for producing the pigment melanin, and the TYRP1 gene, which plays a role in the production of eumelanin and pheomelanin. These two pigments determine the color of our hair, with eumelanin producing dark colors and pheomelanin producing red and blonde shades. However, the exact combination of these genes can vary from person to person, leading to a wide range of hair colors.
The Dominance of Blonde Hair Genes
 Out of all the hair colors, blonde hair is considered to be the most dominant. This is because the gene for blonde hair, known as the "blonde gene," is a mutated version of the gene that produces red hair. This means that if someone has inherited the blonde gene from one parent and the red hair gene from the other, their hair will appear blonde. In contrast, if someone has inherited the blonde gene from one parent and the dark hair gene from the other, their hair will still appear blonde.
This dominance of the blonde gene also explains why blonde hair is more common in certain regions, such as Scandinavia and Northern Europe. These areas have a higher prevalence of the blonde gene, leading to a higher percentage of people with blonde hair. Additionally, the blonde gene can also be found in other regions, as it can be passed down from ancestors who migrated from these areas.
Out of all the hair colors, blonde hair is considered to be the most dominant. This is because the gene for blonde hair, known as the "blonde gene," is a mutated version of the gene that produces red hair. This means that if someone has inherited the blonde gene from one parent and the red hair gene from the other, their hair will appear blonde. In contrast, if someone has inherited the blonde gene from one parent and the dark hair gene from the other, their hair will still appear blonde.
This dominance of the blonde gene also explains why blonde hair is more common in certain regions, such as Scandinavia and Northern Europe. These areas have a higher prevalence of the blonde gene, leading to a higher percentage of people with blonde hair. Additionally, the blonde gene can also be found in other regions, as it can be passed down from ancestors who migrated from these areas.
The Role of Genetics in Hair Color
 While the blonde gene may be dominant, it is not the only factor that determines hair color. Other genes, such as those responsible for producing melanin, also play a role. This is why siblings can have different hair colors, even if they have the same parents. It all depends on the combination of genes that each parent passes down to their child.
In conclusion, the dominance of blonde hair genes can be attributed to a combination of genetics and mutations in the MC1R gene. This gene plays a significant role in determining hair color and can result in a wide range of shades, including blonde. So the next time you see someone with a head of blonde hair, you can appreciate the science behind it.
While the blonde gene may be dominant, it is not the only factor that determines hair color. Other genes, such as those responsible for producing melanin, also play a role. This is why siblings can have different hair colors, even if they have the same parents. It all depends on the combination of genes that each parent passes down to their child.
In conclusion, the dominance of blonde hair genes can be attributed to a combination of genetics and mutations in the MC1R gene. This gene plays a significant role in determining hair color and can result in a wide range of shades, including blonde. So the next time you see someone with a head of blonde hair, you can appreciate the science behind it.