Blonde hair has captivated people for centuries, from the golden locks of ancient goddesses to the iconic hair color of Hollywood stars. But what is the genetic basis behind this coveted hair color? Let's dive into the science of blonde hair genetics and uncover the fascinating facts behind it.Genetic Basis of Blonde Hair
The genetics of blonde hair is a complex and ever-evolving topic. However, researchers have identified several genes that play a key role in determining hair color. One of the main genes involved is MC1R, also known as the "ginger gene", which controls the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for hair color.Blonde Hair Genetics: What We Know So Far
The MC1R gene comes in various forms, or alleles, which can be inherited from both parents. If both parents have a mutated form of this gene, their offspring have a higher chance of inheriting blonde hair. However, even if only one parent carries this gene, there is still a possibility of having blonde hair, although it may be a lighter or darker shade.The Science Behind Blonde Hair
Blonde hair color is not just determined by MC1R, but also by other genes that influence the production and distribution of melanin. These include TYRP1, which affects the amount of red and yellow pigments in hair, and OCA2, which plays a role in the production of melanin in the eyes, skin, and hair.Exploring the Genetics of Blonde Hair Color
Interestingly, blonde hair is not just limited to individuals of European descent. Research has shown that people of Melanesian and Polynesian descent also have a high prevalence of blonde hair, despite having different genetic variations compared to Europeans. This suggests that blonde hair may have evolved independently in different populations.Genetic Variations Associated with Blonde Hair
As mentioned earlier, melanin is the main pigment responsible for hair color. People with blonde hair have lower levels of melanin compared to those with darker hair colors, resulting in lighter hair. However, the distribution of melanin also plays a role in the final hair color. For example, individuals with a higher concentration of melanin in the cortex of their hair tend to have darker blonde hair.The Role of Melanin in Blonde Hair Genetics
While many people dye their hair blonde, there are also those who are lucky enough to be born with natural blonde hair. So, what are the genetic factors behind this hair color? Research has shown that blondes have a higher prevalence of TYRP1 and OCA2 gene variants, which contribute to the production and distribution of melanin.Understanding the Genetics of Natural Blonde Hair
Aside from genes, there are also external factors that can influence the expression of blonde hair. Sun exposure, for example, can lighten hair color due to the breakdown of melanin. On the other hand, certain medications or medical conditions can also affect the production of melanin, causing a change in hair color.Genetic Factors Influencing Blonde Hair Color
As you can see, the genetics of blonde hair is a complex and multifactorial process. From inherited gene variations to environmental influences, there are many factors that determine the final hair color. But one thing is for sure, blonde hair will continue to fascinate and inspire us for generations to come.The Genetics of Blonde Hair: A Comprehensive Review
We've covered the genetic basis of blonde hair, but what about its inheritance and expression? According to Mendelian genetics, blonde hair is a recessive trait, meaning both parents must carry the gene for it to be expressed in their offspring. However, with the discovery of multiple genes involved in hair color, the inheritance of blonde hair can be more complex than previously thought.Blonde Hair Genetics: From Inheritance to Expression
The Genetics of Blonde Hair: Understanding the Science Behind this Coveted Hair Color

The Basics of Hair Color Genetics
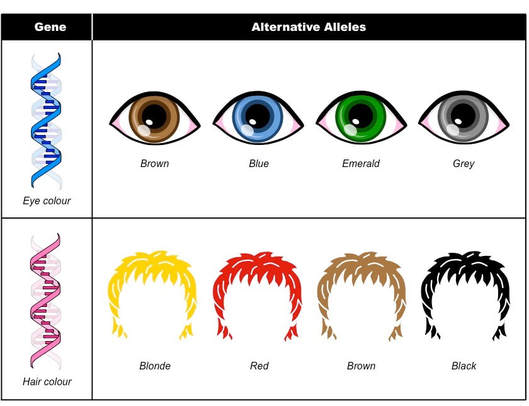
 When it comes to hair color, there are two main types of pigment that determine the shade of our locks: eumelanin and pheomelanin. Eumelanin is responsible for darker hair colors such as brown and black, while pheomelanin is responsible for lighter hair colors like red and blonde. These pigments are produced by specialized cells called melanocytes and are controlled by a variety of genetic factors.
When it comes to hair color, there are two main types of pigment that determine the shade of our locks: eumelanin and pheomelanin. Eumelanin is responsible for darker hair colors such as brown and black, while pheomelanin is responsible for lighter hair colors like red and blonde. These pigments are produced by specialized cells called melanocytes and are controlled by a variety of genetic factors.
Blonde Hair: A Recessive Trait
 Blonde hair is considered a recessive trait, meaning that it is only expressed when an individual inherits two copies of the gene responsible for producing pheomelanin.
This gene, known as MC1R, codes for a protein that regulates the production of melanin. When an individual inherits two copies of the "blonde" version of this gene, they will have little to no eumelanin in their hair, resulting in a lighter hair color.
Blonde hair is considered a recessive trait, meaning that it is only expressed when an individual inherits two copies of the gene responsible for producing pheomelanin.
This gene, known as MC1R, codes for a protein that regulates the production of melanin. When an individual inherits two copies of the "blonde" version of this gene, they will have little to no eumelanin in their hair, resulting in a lighter hair color.
The Role of Melanin in Hair Color
 Melanin not only determines the shade of our hair, but it also affects the texture and thickness of our locks.
Individuals with blonde hair have less melanin in their hair, making it finer and more prone to damage from sunlight and other environmental factors.
This is why many people with blonde hair have fair skin and freckles, as their skin also lacks melanin and is more sensitive to UV radiation.
Melanin not only determines the shade of our hair, but it also affects the texture and thickness of our locks.
Individuals with blonde hair have less melanin in their hair, making it finer and more prone to damage from sunlight and other environmental factors.
This is why many people with blonde hair have fair skin and freckles, as their skin also lacks melanin and is more sensitive to UV radiation.
The Influence of Other Genes
 While MC1R is the main gene responsible for blonde hair, there are other genetic factors that can influence hair color. For example, variations in the gene OCA2 can also affect the amount of melanin produced by melanocytes, leading to different shades of blonde hair. Additionally, genes involved in hair texture and thickness, such as KRT71 and TCHH, can also play a role in determining the appearance of blonde hair.
While MC1R is the main gene responsible for blonde hair, there are other genetic factors that can influence hair color. For example, variations in the gene OCA2 can also affect the amount of melanin produced by melanocytes, leading to different shades of blonde hair. Additionally, genes involved in hair texture and thickness, such as KRT71 and TCHH, can also play a role in determining the appearance of blonde hair.
The Evolution of Blonde Hair
 While blonde hair is often associated with Northern European ancestry, it is actually a relatively recent genetic adaptation. It is believed that
blonde hair evolved in response to a lack of sunlight in these regions, as lighter hair and skin allowed for better absorption of vitamin D.
As humans migrated to areas with more sunlight, the genetic mutation for blonde hair became less advantageous and thus, less common.
While blonde hair is often associated with Northern European ancestry, it is actually a relatively recent genetic adaptation. It is believed that
blonde hair evolved in response to a lack of sunlight in these regions, as lighter hair and skin allowed for better absorption of vitamin D.
As humans migrated to areas with more sunlight, the genetic mutation for blonde hair became less advantageous and thus, less common.
In Conclusion
 While the genetics behind blonde hair may seem complex, one thing is clear:
blonde hair is a recessive trait that is influenced by a variety of genetic factors.
Understanding the science behind this coveted hair color can not only satisfy our curiosity, but it can also help us appreciate the diversity and complexity of human genetics.
While the genetics behind blonde hair may seem complex, one thing is clear:
blonde hair is a recessive trait that is influenced by a variety of genetic factors.
Understanding the science behind this coveted hair color can not only satisfy our curiosity, but it can also help us appreciate the diversity and complexity of human genetics.